China’s Export Expansion Hits Four-Month Low Amid Trade Barriers
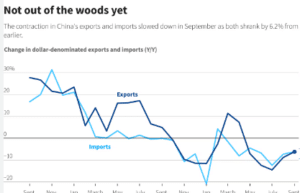
China’s export growth is set to slow to its weakest pace in four months, as rising global trade tensions and cooling demand weigh heavily on the world’s second-largest economy. According to a Reuters poll, trade data expected for Tuesday is forecast to reveal a 6.5% year-on-year increase in exports by value for August. This marks a decline from July’s 7.0% growth rate and underscores the growing economic headwinds China faces.
Key Data and Trends:
- Export Growth: Analysts anticipate a 6.5% increase in August exports, a slowdown from the 7.0% recorded in July. This deceleration reflects diminished global demand and increasing trade barriers impacting China’s export performance.
- Import Growth: Inbound shipments are projected to grow by only 2% in August, a dramatic drop from July’s 7.2% growth. The previous month’s surge was driven by a rush to stockpile semiconductors in anticipation of U.S. technology restrictions.
- Tech Imports Indicator: South Korea, a key barometer for China’s tech imports, reported a slower pace of exports to China in August following a 21-month high in July.
Economic Challenges and Trade Risks:
- Manufacturing Decline: China’s manufacturing sector has contracted for six consecutive months, with factory gate prices plummeting to their lowest levels in 14 months. The expected slowdown in imports highlights waning domestic demand amid ongoing challenges in the housing market and rising job insecurities.
- Fiscal Measures: Despite these setbacks, there is cautious optimism that increased fiscal spending could stimulate economic growth in the latter half of the year. While exports may maintain some resilience, the economic outlook remains uncertain.
- Rising Trade Tensions: Trade relations are further strained by escalating tariffs. Canada recently imposed a 100% tariff on Chinese electric vehicle imports, joining the U.S. and European Union in intensifying trade measures against China. Additionally, India’s steel ministry is advocating for higher tariffs on steel imports from China, and Malaysia has initiated an anti-dumping probe into Chinese and Indonesian plastic products.
Trade Surplus Forecast:
China’s trade surplus for August is estimated at $82.05 billion, a slight decrease from July’s $84.65 billion. This forecast reflects anticipated declines in both exports and imports.
Outlook and Implications:
The anticipated slowdown in China’s export growth signals a potential end to the peak export momentum, as tariffs and trade disputes increasingly impact economic performance. Moving forward, China’s ability to navigate these challenges through fiscal policies and export resilience will be crucial for stabilizing the economy.
Stay informed with the latest updates and in-depth analysis by subscribing to the Reuters Daily Briefing newsletter.
China’s Export Growth Slows to Four-Month Low as Trade Barriers Intensify
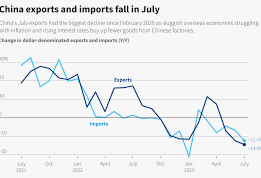
China’s export growth is expected to decelerate to its slowest pace in four months, highlighting the mounting challenges faced by the world’s second-largest economy. According to a Reuters poll, trade data due for release on Tuesday is forecast to show a 6.5% year-on-year increase in August exports by value. This represents a slowdown from the 7.0% growth recorded in July and signals the impact of deteriorating global economic conditions and escalating trade tensions.

Detailed Economic Indicators:
Export Data:
- Forecast Growth: Exports are projected to rise by 6.5% in August compared to the same month last year. This figure marks a noticeable drop from July’s 7.0% growth rate, reflecting diminishing external demand and the strain of increased trade restrictions.
- Sector Impact: Key export sectors, including electronics and machinery, are experiencing a slowdown due to weakened global demand and supply chain disruptions.
Import Data:
- Forecast Growth: Imports are anticipated to increase by 2% in August, a sharp decline from July’s 7.2% growth. The significant drop is attributed to reduced domestic consumption and a slowdown in semiconductor stockpiling, which was driven by anticipated U.S. technology restrictions.
- Tech Imports: South Korea, a significant supplier of tech components to China, reported a slower growth rate in exports to China in August, down from a 21-month high in July. This suggests reduced demand for tech imports from China.
Manufacturing and Domestic Demand:
- Manufacturing Sector: August marks the sixth consecutive month of contraction in manufacturing activity in China. Factory gate prices have fallen to their lowest levels in 14 months, signaling ongoing deflationary pressures within the production sector.
- Domestic Consumption: The slowdown in imports highlights weak domestic demand, exacerbated by a prolonged slump in the housing market and rising job insecurities.

Fiscal and Policy Measures:
- Fiscal Spending: There is cautious optimism that increased fiscal spending and infrastructure investments could provide a boost to economic growth in the latter half of the year. However, the effectiveness of these measures in countering the slowdown remains uncertain.
- Export Resilience: Despite current challenges, exports are expected to retain some level of resilience, although overall growth may be constrained by external pressures and trade disputes.
Escalating Trade Tensions:
- Tariffs and Trade Barriers: Trade tensions continue to escalate with new tariffs and trade measures. Canada recently imposed a 100% tariff on imports of Chinese electric vehicles, adding to existing trade restrictions from the U.S. and European Union. India is pushing for higher tariffs on steel imports from China, and Malaysia has initiated an anti-dumping investigation into Chinese and Indonesian plastic products.
- Impact on Export Momentum: Analysts, including Oxford Economics, warn that the peak of Chinese export momentum may have passed. Supportive price factors are expected to diminish as new tariffs come into effect, potentially dampening export performance.
Trade Surplus Forecast:
- Projected Surplus: China’s trade surplus for August is forecast at $82.05 billion, down slightly from $84.65 billion in July. This decrease reflects the anticipated slowdown in export growth and the decline in import growth.
Conclusion and Outlook: The anticipated slowdown in China’s export growth underscores the challenges posed by rising trade barriers and weakening global demand. As China navigates these obstacles, fiscal policy adjustments and export resilience will be critical in shaping the country’s economic trajectory. The ability to adapt to escalating trade tensions and bolster domestic economic activity will be essential for stabilizing growth.v