SEO Keywords: China exports August 2024, Chinese economic growth, global trade tensions, China import data, U.S.-China trade relations, China EU trade, rare earths trade China, China automotive exports, Chinese economy, global economic slowdown, domestic demand China, China trade policy, China market outlook.
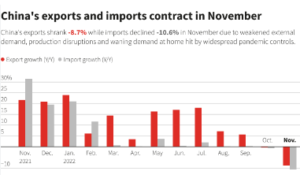
Beijing, September 9, 2024 — In a remarkable display of economic resilience, China’s export sector outperformed expectations in August, with exports surging by 8.7% year-on-year in U.S. dollar terms. This impressive growth, reported by China’s customs agency, significantly exceeded the 6.5% rise anticipated by analysts, highlighting China’s enduring strength in global trade amid widespread economic uncertainties.
Key Drivers Behind the Export Boom
China’s robust export performance was driven by substantial gains across key sectors and major trading partners. Exports to the European Union (EU) saw the most significant increase, soaring by 13% year-on-year, while shipments to the United States and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) also posted strong growth.
Several industries were at the forefront of this export surge:
- Automotive Sector: Car exports skyrocketed by nearly 40% in August, reaching 610,000 vehicles, reinforcing China’s growing influence in the global automotive market.
- Shipbuilding Industry: The export of ship vessels also climbed by 40%, showcasing China’s prowess in this critical sector.
- Consumer Electronics: Exports of smartphones increased by 6.7%, while suitcase exports rose by nearly 9%, underscoring China’s dominance in consumer goods.
- High-Tech Components: The value of integrated circuits exported surged by 18%, solidifying China’s central role in the global technology supply chain.
- Mixed Signals from Import Data
- While exports thrived, China’s import growth was notably subdued, increasing by just 0.5% year-on-year in U.S. dollar terms, far below the 2% rise predicted by experts. This marks a sharp deceleration from July’s stronger performance, raising concerns about weakening domestic demand.
- China’s imports from the United States rose by 12%, while imports from the EU declined. Notably, imports from Russia fell by 1%, while imports from ASEAN increased by 5%. A significant drop was also observed in crude oil imports, which fell by 7% in volume, reflecting shifting dynamics in global energy markets.
- Challenges in the Rare Earths Trade
- China’s rare earths trade—a sector of critical strategic importance—faced headwinds in August. Export volumes of rare earths dropped by 1%, while imports plummeted by 12%, coinciding with China’s new policies aimed at tightening control over its rare earths industry. These measures, driven by national security concerns, include upcoming export controls on antimony, set to take effect later this month.
- Economic Outlook: Domestic Demand Under the Microscope
- Despite the unexpected strength in exports, China’s broader economic outlook remains clouded by concerns over domestic demand. Steve Brice, Chief Investment Officer at Standard Chartered Wealth Management, emphasized that import performance is a key indicator of China’s internal economic health. “The focus is on whether China can generate sufficient domestic demand to avoid a deflationary cycle,” Brice remarked on CNBC’s “Street Signs Asia.”
This concern is particularly pressing given the potential for escalating trade tensions with the United States, especially if the upcoming U.S. presidential election leads to a reintroduction of tariffs on Chinese goods.
Market Reaction and Anticipated Economic Data
In response to the mixed economic signals, mainland Chinese stocks traded lower on Tuesday, reflecting investor caution. The markets are now keenly awaiting the release of key economic indicators, including retail sales, industrial production, and investment data for August, which are scheduled for publication on Saturday. These figures will provide crucial insights into the health of China’s economy and its ability to sustain growth amid global challenges.
Adding to the economic concerns, the core consumer price index (CPI)—which excludes volatile food and energy prices—rose by just 0.3% year-on-year in August. This represents the slowest pace of growth since March 2021, further fueling worries about weak domestic demand and potential deflationary pressures.
Rising Global Trade Tensions
China’s increasing reliance on exports comes at a time of heightened global trade tensions. Both the United States and the European Union have recently imposed additional tariffs on Chinese products, including electric vehicles, as part of broader concerns about trade imbalances and market competition.
As China navigates these complex challenges, the economic performance of the world’s second-largest economy will continue to be a focal point for global markets, policymakers, and businesses. The ongoing trade disputes and internal economic struggles raise critical questions about China’s future growth trajectory and its role in the global economy.
1. Detailed Trade Partner Analysis
- United States: Explore the trade dynamics between China and the U.S., focusing on key exports such as electronics, machinery, and textiles. Highlight any recent shifts in trade patterns, particularly in the context of ongoing trade tensions and tariffs.
- European Union: Analyze the growth in exports to the EU, emphasizing which sectors are driving this increase. Consider discussing the impact of EU regulations on Chinese exports and the broader implications of the EU’s trade policies.
- ASEAN: Delve into the growing economic ties between China and ASEAN countries, highlighting the importance of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) in facilitating trade.
- 2. Sector-Specific Insights
- Automotive Exports: Provide more context on why automotive exports surged by 40%. Discuss the role of Chinese electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers, the global demand for EVs, and how China’s automotive industry is competing on the global stage.
- Consumer Electronics: Break down the specific categories of consumer electronics driving export growth. Discuss trends in global demand for smartphones, laptops, and other consumer electronics, and how Chinese manufacturers are positioning themselves in these markets.
- High-Tech Components: Discuss China’s role in the global semiconductor supply chain, focusing on the export of integrated circuits. Highlight how China’s technological advancements and government policies are influencing this sector.
- 3. Import Weakness and Domestic Economy
- Factors Behind Weak Import Growth: Investigate the reasons for the sluggish import growth. Consider factors such as weak domestic consumption, ongoing economic uncertainties, and the impact of the Chinese government’s policies on imports.
- Crude Oil Imports: Analyze the decline in crude oil imports, exploring whether this is due to decreased industrial activity, energy conservation efforts, or shifts in global oil prices. Include data on China’s overall energy consumption trends.
- Impact on Manufacturing and Retail: Discuss how weak import growth might reflect broader economic issues in China, such as sluggish manufacturing output, low consumer confidence, and challenges in the retail sector.
- . Rare Earths Industry
- Strategic Importance: Explain the strategic importance of rare earths in global technology and defense industries. Discuss how China’s dominance in this market gives it leverage in trade negotiations and impacts global supply chains.
- Government Policies: Elaborate on China’s new policies aimed at tightening control over the rare earths industry, including export controls on antimony. Discuss how these measures might affect global markets and industries dependent on these critical minerals.
- 5. Economic Indicators and Market Sentiment
- Upcoming Economic Data: Provide a preview of the key economic indicators to be released, such as retail sales, industrial production, and investment data. Discuss how these indicators will shed light on the health of China’s domestic economy.
- Stock Market Analysis: Offer insights into how Chinese stocks have reacted to recent economic data and global market trends. Discuss the broader implications for investors and what future economic reports could mean for market sentiment.
- 6. Global Trade Tensions
- Impact of U.S. Policies: Analyze the potential impact of U.S. trade policies, particularly in light of the upcoming presidential election. Discuss how different outcomes might affect U.S.-China trade relations and China’s export sector.
- EU Trade Policies: Explore the implications of recent EU actions, such as the imposition of tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles, and how they might impact future trade relations between China and the EU.
- Geopolitical Risks: Consider broader geopolitical risks that could affect China’s trade, such as tensions in the South China Sea, relations with Taiwan, and China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- 7. Long-Term Economic Outlook
- Domestic Demand and Consumption: Discuss the challenges China faces in boosting domestic demand, including structural issues in the economy, demographic trends, and consumer behavior. Offer insights into potential policy responses and their effectiveness.
- Technological Innovation: Highlight how technological innovation and digital transformation are shaping China’s economy, particularly in areas like e-commerce, fintech, and green technology. Discuss how these trends might influence future trade patterns.
- Global Economic Impact: Consider the broader global economic implications of China’s export performance, particularly for emerging markets and global supply chains. Discuss how China’s economic policies and performance could impact global growth.
- 8. Visual Data and Infographics
- Export and Import Trends: Include visual data such as charts or infographics that illustrate the trends in China’s exports and imports over the past few years. Highlight key sectors and trade partners.\Rare Earths Trade: Provide a visual breakdown of China’s rare earths production, exports, and imports, showing its dominance in the global market.
- Stock Market Performance: Include a chart showing the performance of major Chinese stock indices in response to recent economic data.
- 9. Expert Opinions and Analysis
- Economist Perspectives: Incorporate quotes and analysis from leading economists and market analysts on China’s export growth and its implications for the global economy.
- Industry Experts: Include insights from industry experts in sectors like automotive, electronics, and rare earths, discussing the factors driving growth and the challenges ahead.
- 10. Related Articles and Resources Deep Dives: Link to related articles that provide a deeper analysis of specific topics mentioned in the article, such as the impact of U.S.-China trade tensions, the role of China in the global semiconductor industry, and the future of China’s automotive sector.
- Resource Guides: Offer readers additional resources, such as reports, studies, and expert analyses, to help them better understand the complexities of China’s economy and trade dynamics.